Make an appointment
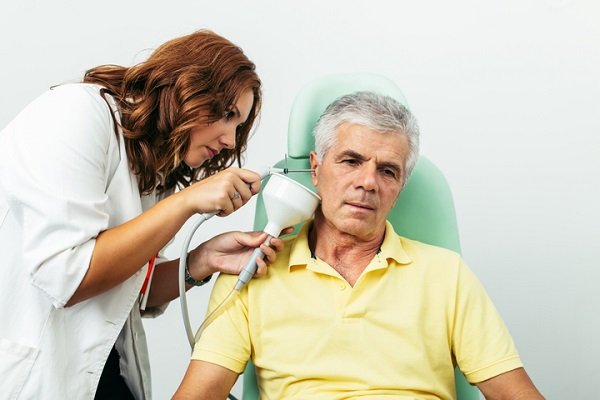
Ear Syringing
Ear Syringing is a medical procedure used to remove excess earwax or debris from the ear canal. It involves flushing the ear with a gentle stream of water or saline solution to dislodge and clear out the wax buildup. This procedure is typically performed by a healthcare professional to prevent damage to the ear or eardrum. Ear syringing is often recommended when earwax causes discomfort, hearing loss, or infection. Before the procedure, the ear is usually softened with ear drops to make the wax easier to remove.
The process may be done with a syringe, a bulb, or a specialized irrigation device. It is generally safe when performed correctly, though it may cause temporary discomfort or dizziness. Ear syringing is not advised for individuals with a history of ear infections, ear drum perforations, or certain medical conditions. After the procedure, patients may experience temporary ear fullness or mild drainage. In some cases, further treatment may be needed if the earwax is impacted or the procedure is ineffective.
Softening the Wax
Before ear syringing, ear drops or oils are often used to soften the wax, making it easier to remove and reducing the risk of injury to the ear canal.
Clears Excess Earwax
Ear syringing is primarily used to remove built-up earwax that may cause discomfort, blockage, or hearing loss, restoring normal ear function

Performed by Healthcare Professionals
Ear syringing should be done by a trained healthcare provider to ensure safety and avoid potential damage to the ear canal or eardrum.
